Welcome Message
Welcome to the official website of the 17th International Conference on Hepatology in 2023, which will be held June 26-27, 2023, Singapore city, Singapore with the theme "Hepatology -Therapeutic Innovations, New Drugs, Approaches, and Investigations."
We cordially invite all medical and clinical experts who are eager to share their research expertise and real-world experience in the fields of hepatology. This is an incredible chance for the representatives from Universities and Institutes to network with top scientists and speakers at our hepatology meeting in 2023 and discuss new developments in engineering and medicine to advance health and treatment, as well as other innovations. We hope you will take advantage of this academic occasion to rekindle old friendships and make new ones with people all across the world.
About Conference
Hepatology is the branch of medicine that incorporates the study of liver, gallbladder, biliary tree, and pancreas as well as management of their disorders. Although traditionally considered a sub-specialty of gastroenterology, rapid expansion has led in some countries to doctors specializing solely on this area, who are called hepatologists.
Diseases and complications related to viral hepatitis and alcohol are the main reason for seeking specialist advice. More than two billion people have been infected with hepatitis B virus at some point in their life, and approximately 350 million have become persistent carriers, Up to 80% of Liver cancers can be attributed to either hepatitis B or hepatitis C virus. In terms of mortality, the former is second only to smoking among known agents causing cancer. With more widespread implementation of vaccination and strict screening blood transfusion, lower infection rates are expected in the future. In many countries, however, overall alcohol consumption is increasing, and consequently the number of people with cirrhosis and other related complications is commensurately increasing.
Session/Tracks
Track 01: Liver Diseases
Liver disease is any disturbance of liver function that causes illness. The liver is responsible for many critical functions within the body and should it become diseased or injured, the loss of those functions can cause significant damage to the body. Liver disease is also referred to as hepatic disease. Liver disease is a broad term that covers all the potential problems that cause the liver to fail to perform its designated functions. Usually, more than 75% or three quarters of liver tissue needs to be affected before a decrease in function occurs.
Types of Liver Diseases including:-
-
Metabolic diseases
-
Autoimmune liver diseases
-
Vascular disorders
-
Genetic Liver Disease
-
Wilson disease
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Track 02: Viral hepatitis
Viral hepatitis is an infection that causes liver inflammation and damage. Inflammation is swelling that occurs when tissues of the body become injured or infected. Inflammation can damage organs. Researchers have discovered several different viruses that cause hepatitis, including:-
-
hepatitis A
-
hepatitis B
-
hepatitis C
-
hepatitis D
-
hepatitis E
Track 03: Cirrhosis of the liver (Alcoholic Liver Disease)
Cirrhosis is a slowly developing disease in which healthy liver tissue is replaced with scar tissue. The scar tissue blocks the flow of blood through the liver and slows the liver’s ability to process nutrients, hormones, drugs and natural toxins (poisons). It also reduces the production of proteins and other substances made by the liver. Cirrhosis eventually keeps the liver from working properly.
-
Fatty liver
-
Alcoholic hepatitis
-
Chronic hepatitis.
Track 04: Hepatic Cysts
Liver cysts are fluid-filled sacs that form in the liver. They’re benign growths, meaning they aren’t cancerous. These cysts generally don’t require treatment unless symptoms develop, and they rarely affect liver function. Liver cysts are the result of a malformation in the bile ducts, although the exact cause of this malformation is unknown. Bile is a fluid made by the liver, which aids in digestion. This fluid travels from the liver to the gallbladder through ducts or tube-like structures.
-
Simple cysts
-
Multiple cysts arising in the setting of polycystic liver disease (PCLD)
-
Parasitic or hydatid (echinococcal) cysts
-
Cystic tumors
-
Abscesses
Ductal cysts, choledochal cysts, and Caroli disease are differentiated from hepatic cysts by involvement of the bile ducts and are not reviewed in this article.
Track 05: Liver Cancer
Liver cancer is cancer that begins in the cells of the liver. The liver is a football-sized organ that sits in the upper right portion of your abdomen, beneath your diaphragm and above your stomach. Cancer that spreads to the liver is more common than cancer that begins in the liver cells. Cancer that begins in another area of the body — such as the colon, lung or breast — and then spreads to the liver is called metastatic cancer rather than liver cancer. This type of cancer is named after the organ in which it began — such as metastatic colon cancer to describe cancer that begins in the colon and spreads to the liver.
Several types of cancer can form in the liver. The most common type of liver cancer is hepatocellular carcinoma, which begins in the main type of liver cell (hepatocyte).
-
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
-
Hepatoblastoma
Track 06: Liver Transplantation
A liver transplant is surgery to replace a diseased liver with a healthy liver from another person. A whole liver may be transplanted, or just part of one. In most cases the healthy liver will come from an organ donor who has just died. Sometimes a healthy living person will donate part of their liver. A living donor may be a family member. Or it may be someone who is not related to you but whose blood type is a good match. People who donate part of their liver can have healthy lives with the liver that is left.
The liver is the only organ in the body that can replace lost or injured tissue (regenerate). The donor’s liver will soon grow back to normal size after surgery. The part that you receive as a new liver will also grow to normal size in a few weeks.
Types of Liver Transplantation
-
Orthotropic transplant
-
Living donor transplant
-
Split type of liver transplant
-
Split type of liver transplant
Track 07: Liver Disease in Pregnancy
Liver disease that occurs during pregnancy can present a challenge for healthcare providers. Certain liver diseases are uniquely associated with pregnancy, whereas others are unrelated. The liver diseases unique to pregnancy include hyperemesis gravidarum, acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP), intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP), and hemolysis and elevated liver enzymes and low platelets (HELLP) syndrome. Liver disease such as acute viral hepatitis can occur in pregnancy, and pregnancy may occur in a patient with underlying chronic liver disease, including patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension, and patients who have undergone liver transplantation.
-
Hyperemesis gravidarum
-
Acute fatty liver of pregnancy (AFLP)
-
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy (ICP
-
Hemolysis
-
Elevated liver enzymes
-
Low platelets (HELLP) syndrome
Track 08: Pancreas and Biliary System
The pancreas and bile duct (biliary) systems together form an important part of the digestive system. The pancreas and liver produce juices (pancreatic juice and bile) which help in the process of digestion (i.e. the breakdown of foods into parts which can be absorbed easily and used by the body.
-
Acute Pancreatitis
-
Alcohol-Related Pancreatitis
-
Cholangitis
-
Cholecystitis
-
Chronic Pancreatitis
-
Diabetes
-
Gallstone Pancreatitis
-
Gallstones and Bile Duct Stones
-
Hereditary Pancreatitis
-
Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm
-
Pancreas Divisum
-
Pancreatic Cancer
-
Pancreatic Insufficiency
-
Pancreatitis
-
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC)
-
Sphincter of Oddi Dysfunction (SOD)
Track 09: Pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancerous) cells form in the tissues of the pancreas. The pancreas is a gland located behind the stomach and in front of the spine. The pancreas produces digestive juices and hormones that regulate blood sugar. Cells called exocrine pancreas cells produce the digestive juices, while cells called endocrine pancreas cells produce the hormones. The majority of pancreatic cancers start in the exocrine cells.
-
Exocrine tumors
-
Neuroendocrine tumors
Track 10: Gallbladder diseases
The gallbladder is a small pouch that sits just under the liver. The gallbladder stores bile produced by the liver. After meals, the gallbladder is empty and flat, like a deflated balloon. Before a meal, the gallbladder may be full of bile and about the size of a small pear. In response to signals, the gallbladder squeezes stored bile into the small intestine through a series of tubes called ducts. Bile helps digest fats, but the gallbladder itself is not essential. Removing the gallbladder in an otherwise healthy individual typically causes no observable problems with health or digestion yet there may be a small risk of diarrhea and fat malabsorption.
Gallbladder diseases considered here include
-
Gallstones,
-
Tumors,
-
Acute a calculous cholecystitis.
Track 11: Disorders of hepatobiliary system
Disorders of the liver and biliary system (which creates and stores bile) may require surgical correction. These disorders can be developmental or congenital, or they may manifest later in childhood or adolescence.
-
Benign gallbladder diseases include infections (cholecystitis) and gallstones causing symptoms (biliary colic).
-
Bile duct cysts (choledochal cysts) stem from abnormal development of the biliary system and have been associated with cancer (cholangiocarcinoma) as well as infection of the bile duct (cholangitis).
-
Biliary atresia can prevent bile from being able to drain from the liver into the intestine. It stems from abnormal development of the biliary system.
Track 12: Hemochromatosis
Hemochromatosis is a disorder where too much iron builds up in the body. Sometimes it’s called “iron overload.” Normally, our intestines absorb just the right amount of iron from the foods we eat. But in hemochromatosis, our body absorbs too much, and it has no way to get rid of it. So, our body stores the excess iron in our joints and in organs like our liver, heart, and pancreas. This damages them. If it’s not treated, hemochromatosis can make our organs stop working.
There are two types of this condition primary and secondary.
-
Primary hemochromatosis
-
Secondary hemochromatosis
Track 13: Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition
Liver diseases are mostly seen as in a grown-up, however, a huge number of children from babies to teens experience from different types of liver diseases. The volume of the liver and the blood flow decreases with age, immune responses against pathogens or neoplastic cells are lower in the elderly reducing their tolerability to treatments for liver diseases. Liver regeneration capacity shows a decline in age, reduced proliferation of hepatocytes, but the level of hepatic enzymes and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol is well maintained. Pediatric hepatology focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of liver and liver-related disease in infants and children.
Track 14: Clinical Research in Hepatology
The journal present up-to-date coverage of basic and clinical researches on molecular and cell biology, pathophysiology, epidermal, diagnosis, and treatment of the various diseases of the liver and biliary tract, B viral hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma are the common liver diseases in Asian-pacific region. Idiosyncratic drug induced liver injury (Dili) is a rare adverse druid reaction and it can lead to jaundice, liver failure, or even death. In the Western world Antimicrobials and herbal and dietary supplements are among the most common therapeutic classes to cause DILI. Liver fibrosis is the excessive accumulation of extra cellular proteins collagen that occurs in most types of chronic liver diseases.
Track 15: Functional GI Disorders
Functional gastrointestinal diseases (FGID) are a group of diseases characterized by habitual gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms (e.g. abdominal pain, dysphagia, dyspepsia, diarrhea, constipation and bloating) in the absence of provable pathology on conventional testing. Some causes of FGIDs are environmental, like stress and smoking, and can be greatly affected by life changes. There are also numerous causes that you have no control over, similar as family history. gut perceptivity. While there are no cures for IBS or functional dyspepsia, neither will beget death nor turn into commodity worse like cancer. Utmost people can learn to control their symptoms by dwindling stress, changing their diet, and occasionally taking drug.
Young Research Forum [YRF]
Young Research Forum (YRF)
Prestigious Award for Young Research’s at Hepatology 2023 – “Hepatology -Therapeutic Innovations, New Drugs, Approaches, and Investigations”
Hepatology 2023 Committee is glad to announce “17th International Conference on Hepatology June 26-27, 2023 in Singapore city, Singapore. Republic and focusing on the theme: “Hepatology -Therapeutic Innovations, New Drugs, Approaches, and Investigations”. Hepatology 2023 developments are maintaining their momentum. Hepatology Conference program delves into strategic discussions.
Hepatology 2023 Young Scientist Awards:
Hepatology 2023 Committee is intended to honour prestigious award for talented Young researchers, scientists, Young Investigators, Post-Graduate students, Post-doctoral fellows, Trainees, Junior faculty in recognition of their outstanding contribution towards the conference theme. The Young Scientist Awards make every effort in providing a strong professional development opportunity for early career academicians by meeting experts to exchange and share their experiences on all aspects of Hepatology.
Young Research’s Awards at Hepatology 2023 for the Nomination: Young Researcher Forum - Outstanding Masters/Ph.D./Post Doctorate thesis work Presentation, only 25 presentations acceptable at the Hepatology 2023 young research forum.
Benefits
-
Young Scientist Award recongination certificate and memento to the winners.
-
Our conferences provide best Platform for your research through oral presentations.
-
Learn about career improvement with all the latest technologies by networking.
-
Young Scientists will get appropriate and timely information by this Forum.
-
Platform for collaboration among young researchers for better development.
-
Provide an opportunity for research interaction and established senior investigators across the globe in the field.
-
Share the ideas with both eminent researchers and mentors.
-
It’s a great privilege for young researchers to learn about the research areas for expanding their research knowledge.
Eligibility
-
Young Investigators, Post-Graduate students, Post-doctoral fellows, Trainees, Junior faculty with a minimum of 5 years of research experience
-
Presentation must be into scientific sessions of the conference.
-
Each Young Researcher / Young Scientist can submit only one paper (as first author or co-author).
-
All submissions must be in English.
Benefits of Joining Conference:
-
Get your abstract published with DOI
-
Get Certified for your participation
-
Reduced Costs Affordability
-
Knock Down Geographical Barriers
-
Convenience from comfort of your own residence or from work
-
Great resource for learning new career skills
-
Learn from the Pros
-
Global exposure to your research
-
Make new connections
-
Significant time saving
-
Increased engagement
-
Wider Reach
-
More Engaging
-
Position yourself because the expert
Market Analysis
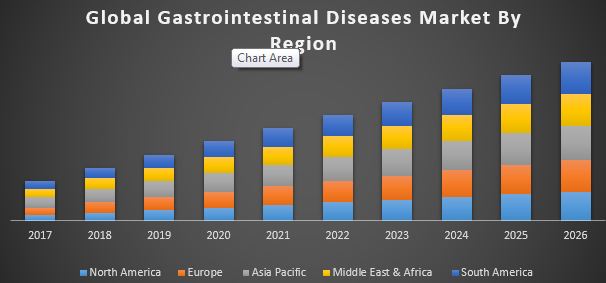
Gastrointestinal Diseases Market valued USD 17.59 Billion in 2017 and expected to reach USD 21.67 Billion by 2026, at a CAGR of 2.64%.
The market for Gastrointestinal Diseases is primarily depended on increasing life expectancy and improved accessibility to healthcare facilities worldwide. Various factors to be considered for Gastrointestinal Diseases include continuous consideration by analysis of patient’s oxygenation, ventilation, blood circulation, and body temperature.
Report includes assessment of Global Gastrointestinal Diseases Market definition along with the identification of key players and analysis of their strategies, complete quantitative analysis of the industry from 2017 to 2026 to enable the stakeholders to capitalize on the prevailing market opportunities, market analysis and comprehensive segmentation with respect to the drug category and geography to assist in strategic business planning.
APAC is expected to register the highest growth rate in Gastrointestinal Diseases Market during forecast period. APAC is expected to lead the Global Gastrointestinal Diseases Market during the forecast period. Growing investments and funding in the field of life science research and advanced therapies for the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases in developing nations such as China and India will fuel the Global Gastrointestinal Diseases Market in APAC region.


















